Heat Pump hot water systems are incredibly cheap, saving people a whopping 75% compared to a electric or LPG gas system and in some cases cheaper than a solar.
Heat pump hot water heaters absorb warmth from the air and transfer it to heat water. They operate on electricity but are roughly three times more efficient than your standard element type conventional electric water heater. When used in the right environment they save energy, save money and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.

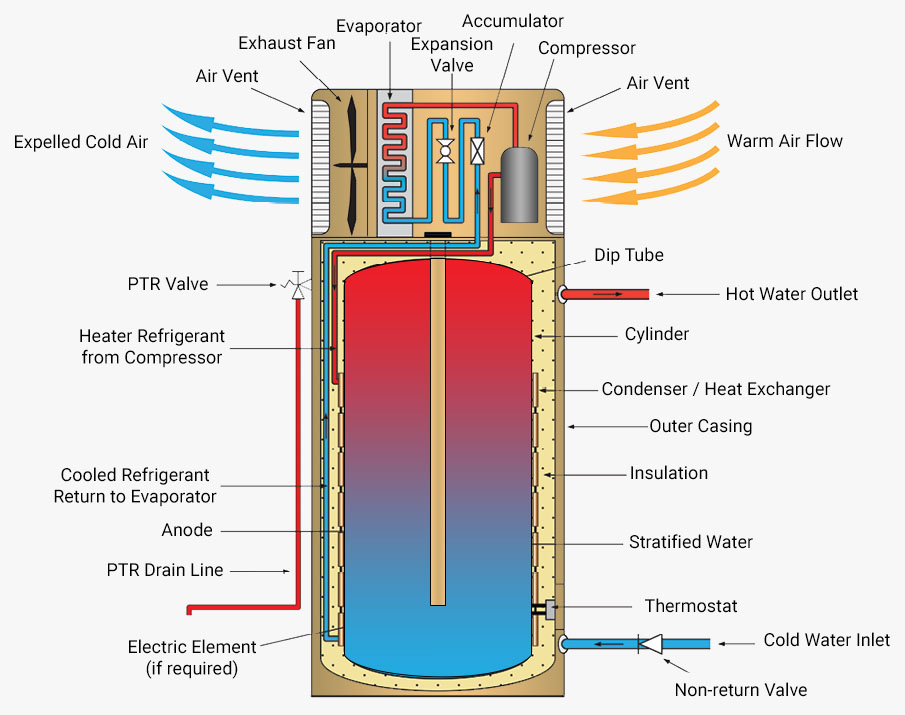
A heat pump works on the same principle as a air conditioner, but instead of pumping heat out to keep it cool, they pump heat into the water via pipes submerged or wrapping storage tanks. Some brands also move the water from the tank through a heating plate to heat the water then back to the storage tank. Electricity is used to pump a refrigerant through the system. The refrigerant transfers the heat absorbed through the air to the water in the tank.
There are several steps in the process:
A heat pump uses electricity to drive the compressor and the fan, unlike a traditional electric resistance water heater that uses electricity to directly heat the water. The heat pump is able to transfer a much greater amount of heat energy from the surrounding air to the water, which makes it highly efficient. The amount of heat that is able to be transferred from the air to water depends on the ambient temperature.
In order for the evaporator to allow heat to be absorbed continuously, there needs to be a constant supply of fresh air. A fan is used to force air flow through and the colder air is removed to the atmosphere
Two different styles of heat pump water heaters
Integrated or compact design where the compressor and the storage tank are a single complete system.
Split systems where the tank and the compressor are 2 separate items, like a split air conditioner, where the storage tank is connected to the heat pump component by refrigerate pipes.















